 Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries
...one of the most highly
regarded and expertly designed C++ library projects in the
world.
— Herb Sutter and Andrei
Alexandrescu, C++
Coding Standards
 Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries
...one of the most highly
regarded and expertly designed C++ library projects in the
world.
— Herb Sutter and Andrei
Alexandrescu, C++
Coding Standards
Bidirectional maps may have associated information about each relation. Suppose we want to represent a books and author bidirectional map.
typedef bimap< multiset_of< std::string >, // author set_of< std::string > // title > bm_type; typedef bm_type::value_type book; bm_type bm; bm.insert( book( "Bjarne Stroustrup" , "The C++ Programming Language" ) ); bm.insert( book( "Scott Meyers" , "Effective C++" ) ); bm.insert( book( "Andrei Alexandrescu" , "Modern C++ Design" ) ); // Print the author of Modern C++ std::cout << bm.right.at( "Modern C++ Design" );
Suppose now that we want to store abstract of each book. We have two options:
std::map< string, string >
that relates books names with abstracts.
Option 1 is the wrong approach, if we go this path we lost what bimap has won us. We now have to maintain the logic of two interdependent containers, there is an extra string stored for each book name, and the performance will be worse. This is far away from being a good solution.
Option 2 is correct. We start thinking books as entries in a table. So it makes sense to start using Boost.MultiIndex. We can then add the year of publication, the price, etc... and we can index this new items too. So Boost.MultiIndex is a sound solution for our problem.
The thing is that there are cases where we want to maintain bimap semantics
(use at()
to find an author given a book name and the other way around) and add information
about the relations that we are sure we will not want to index later (like
the abstracts). Option 1 is not possible, option 2 neither.
Boost.Bimap provides support for this kind of situations by means of an embedded
information member. You can pass an extra parameter to a bimap: with_info<
InfoType >
and an info member of type
InfoType will appear in the
relation and bimap pairs.
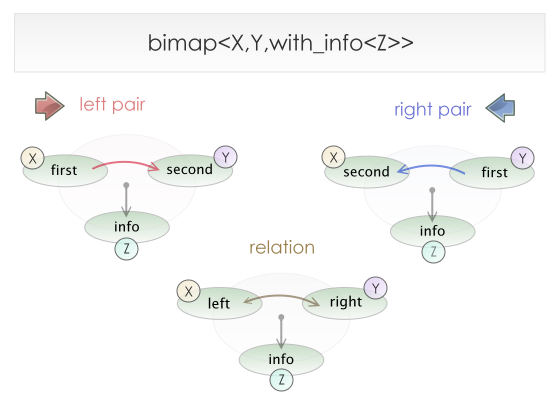
Relations and bimap pairs constructors will take an extra argument. If only two arguments are used, the information will be initialized with their default constructor.
typedef bimap< multiset_of< std::string >, // author set_of< std::string >, // title with_info< std::string > // abstract > bm_type; typedef bm_type::value_type book; bm_type bm; bm.insert( book( "Bjarne Stroustrup" , "The C++ Programming Language", "For C++ old-timers, the first edition of this book is" "the one that started it all—the font of our knowledge." ) ); // Print the author of the bible std::cout << bm.right.at("The C++ Programming Language"); // Print the abstract of this book bm_type::left_iterator i = bm.left.find("Bjarne Stroustrup"); std::cout << i->info;
Contrary to the two key types, the information will be mutable using iterators.
i->info += "More details about this book";
A new function is included in unique map views: info_at(key), that
mimics the standard at(key) function
but returned the associated information instead of the data.
// Print the new abstract std::cout << bm.right.info_at("The C++ Programming Language");
The info member can be tagged just as the left or the right member. The following is a rewrite of the above example using user defined names:
typedef bimap< multiset_of< tagged< std::string, author > >, set_of< tagged< std::string, title > >, with_info< tagged< std::string, abstract > > > bm_type; typedef bm_type::value_type book; bm_type bm; bm.insert( book( "Bjarne Stroustrup" , "The C++ Programming Language", "For C++ old-timers, the first edition of this book is" "the one that started it all—the font of our knowledge." ) ); // Print the author of the bible std::cout << bm.by<title>().at("The C++ Programming Language"); // Print the abstract of this book bm_type::map_by<author>::iterator i = bm.by<author>().find("Bjarne Stroustrup"); std::cout << i->get<abstract>(); // Contrary to the two key types, the information will be mutable // using iterators. i->get<abstract>() += "More details about this book"; // Print the new abstract std::cout << bm.by<title>().info_at("The C++ Programming Language");